




Call options are a type of financial derivative that provides the buyer with the right, but not the obligation, to purchase an underlying asset at a specified price within a predetermined timeframe. This versatile investment tool has gained significant popularity among investors due to its potential for substantial profits and limited risk exposure.
One primary reason investors consider buying call options is their ability to amplify returns on investment. By purchasing a call option, an investor gains exposure to the price movements of an underlying asset while investing only a fraction of its actual cost. This leverage allows traders to control larger positions in the market than they would have been able to with their available capital alone.
Understanding Call Options
Call options are financial derivatives that provide investors with the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specific asset, such as stocks or commodities, at a predetermined price within a specified period. They offer an opportunity for investors to profit from an upward movement in the underlying asset’s price without actually owning it. The key elements of call options are the strike price, expiration date, and premium.
The strike price is the predetermined price at which the option holder can buy the underlying asset. The expiration date determines when the option expires and can no longer be exercised. The premium is the cost of buying an option and represents its intrinsic value plus any time value. One primary reason to consider buying call options is leverage. By investing in call options rather than purchasing the underlying asset outright, investors can control a larger number of assets for a fraction of their market value.
How Do Call Options Work vs. Buying a Stock
Buying a stock is different from buying an option. The easiest way to state the difference is that buying a stock is buying something outright, while buying an option is buying the right to buy something.
To reiterate, a call option is a contract that gives the buyer or holder the right to buy an underlying stock for a pre-determined strike price during a pre-specified period that ends at the expiration date. As with any transaction, there are two sides here: the buyer or contract holder (who holds the right to buy the stock) and the seller or writer (who has the obligation to sell the stock). This means any investor can buy or sell call options. However, we’ll focus on the buyer’s side for now and discuss the selling call options in another article.
When buying an option, the buyer pays the seller or writer a premium. This premium is usually denoted as per share, so you’ll see them like this on options trading platforms or websites like Barchart.com:
Remember that all options represent 100 shares of the underlying stock, so the premium seen here will be multiplied by 100 for every contract, which will represent the full premium payment for the call option. For this reason, call options are much more flexible than stock prices. This arrangement allows traders and investors to gain more leverage than what they would get if they just outright buy 100 shares of the stock.
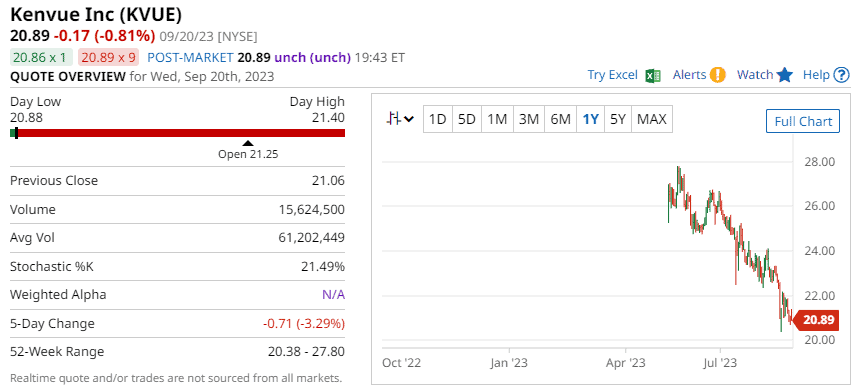
To illustrate this point, let’s take Kenvue Inc. (KVUE) and compare buying stocks to buying options. We can see on the stock chart that KVUE has had a rough few months. If a trader is willing to bet that prices have bottomed out, they might be inclined to buy. And let’s suppose the trader has $2,100 burning a hole in their pocket.
Buying KVUE Stocks
The trader managed to buy KVUE for $20.50 each. The initial cost is $2,050 total ($20.50 x 100) before transaction fees, leaving $50 to spare.
If the price of KVUE rises to $25, the trader can earn a $ 4.50 profit per share or $450 total if they sell the position. This is a 22% profit, which is not bad for stock trading.
Buying KVUE Options
Alternatively, the trader can buy call options (or long calls) with a $20.50 strike price for a maximum of $0.50 per share or $500 total, which expires on September 22 as per Option Samurai. With $2,100 at their disposal, the trader can buy 4 call options worth $2,000 total, giving them control over 400 KVUE stocks, with $100 left over.
Now, if KVUE’s price rises to $25 on or before September 22, the trader can exercise their call option, buy the stock at $20.50 each regardless of market price, and sell it for $25, netting them $4.50 per share. Since they control 400 shares, their total profit will be $10,000. This is a 476% profit. If the trader cannot cover the cost of purchasing 400 KVUE stocks for $20.50 each, they can sell the call option to another buyer instead.
Advantages Of Buying Call Options
The following are some key advantages of buying call options:
1. Limited Risk, Unlimited Potential: One of the most significant advantages of buying call options is the limited risk involved. When purchasing a call option, the maximum loss is limited to the premium paid for the option contract, and this is realized when the option expires worthless. This gives investors peace of mind, as their potential losses are predetermined. On the other hand, call options also offer unlimited profit potential if the underlying asset’s price rises significantly.
2. Leverage: Call options give traders leverage, allowing them to control a larger position in an underlying asset than buying it outright. Investors can participate in market movements without tying up substantial capital by paying only a fraction of the actual cost upfront (the premium).
3. Hedging Opportunities: Call options can be used as an effective hedging tool against existing positions in stocks or other assets. For instance, if an investor holds shares that they believe may decline in value over a specific period, they can purchase call options to offset potential losses or even profit from any upward movement during that period.
4. Diversification: Buying call options enables investors to diversify their portfolios and gain exposure to different sectors or industries without directly owning stocks or other assets within those sectors.
5. Flexibility: Call options provide flexibility in terms of investment horizon and strategy implementation. Investors have the freedom to choose expiration dates and strike prices that align with their investment objectives and market expectations.
6. Lower Capital Requirement: Compared to purchasing shares outright, buying call options requires significantly less capital upfront while still offering exposure to potential price appreciation.
Leveraging Your Investment
One of the primary benefits of buying call options is the ability to leverage your investment. When you purchase call options, you are essentially controlling a larger asset position than what you would be able to afford if you were buying the underlying asset outright. This leverage allows investors to achieve greater exposure and potential profits while committing only a fraction of the capital required for direct ownership.
Furthermore, call options offer limited risk exposure compared to other investment strategies. Since call option buyers have the right but not the obligation to exercise their option, they can limit their losses to the premium paid for purchasing the option contract. This limited risk makes call options attractive for investors looking for potential gains while minimizing downside risk.
Another advantage of leveraging your investment with call options is the opportunity for substantial returns during market upswings. As stock prices rise above the strike price of your call option, its value increases exponentially due to its inherent leverage. This means that even small percentage gains in stock prices can result in significant profits for call option holders.
Additionally, by using call options, investors can participate in markets that may otherwise be inaccessible or expensive through direct ownership. For instance, investing in high-priced stocks or indices may require substantial capital outlay and pose higher risks. However, by purchasing call options on these assets instead, investors can gain exposure without tying up large amounts of capital or taking on excessive risks.
Hedging Against Downside Risk
Call options provide investors with a powerful tool to hedge against downside risk in their portfolios. By purchasing call options, investors can protect their investments from potential losses while still benefiting from any potential upside.
One of the primary advantages of using call options for hedging is the limited risk they offer. This means that if the price of the underlying asset falls significantly, the investor can simply choose not to exercise their option and limit their loss to the premium paid for purchasing the option. This limited risk feature makes call options attractive for hedging against downward movements in stock prices.
Another benefit of using call options for hedging is that they allow investors to participate in any potential upside gains. While traditional forms of hedging, such as selling stocks short or buying put options, only protect against downside risk, call options allow investors to maintain their exposure to potential market gains. If the price of the underlying asset increases significantly, investors can exercise their call option and profit from this upward movement.
Furthermore, call options provide flexibility in managing downside risk. Investors can choose different strike prices and expiration dates based on their individual risk tolerance and investment objectives. This allows them to tailor their hedging strategy according to specific market conditions or events that may affect their portfolio.
Are Trade Options More Versatile?
Call options provide investors with unique flexibility and versatility that can greatly enhance their investment strategies. These financial instruments grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy an underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. This characteristic offers several advantages for traders looking to maximize their potential returns while minimizing risk.
One of the key benefits of call options is their ability to leverage investments. By purchasing call options, traders can control a larger position in the underlying asset than they would be able to by directly buying it. This leverage allows investors to amplify their profits if the price of the asset rises significantly. For example, if an investor purchases call options for a stock with a strike price of $50 and the stock’s value increases to $60, they can exercise their option and buy shares at $50, then sell them immediately at market value, resulting in a profit.
Moreover, call options offer flexibility in terms of timing. Unlike buying stocks outright, where investors are required to hold onto them until they decide to sell, call options have expiration dates. This feature enables traders to take advantage of short-term market movements without committing to long-term positions. If an investor anticipates that the price of an asset will rise in the near future but is uncertain about its long-term prospects, they can purchase call options with shorter expiry dates and capitalize on short-term gains.
Furthermore, call options allow investors to hedge against potential losses in their existing portfolios. If an investor holds shares of a particular stock and expects its value might decline due to upcoming events or market conditions, they can buy corresponding call options as insurance against such losses. In this way, if the stock does decrease in value as predicted, any losses incurred on those shares may be offset by gains from exercising the call option.
Factors To Consider When Buying Call Options
Call options are derivative contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specific asset (such as stocks or commodities) at a predetermined price within a specified period. Buying call options can be an attractive investment strategy for traders seeking to profit from upward price movements in the underlying asset. However, several factors should be considered before engaging in call option transactions.
1. Market Outlook: A crucial factor when buying call options is having a positive market outlook for the underlying asset. It is essential to assess the fundamental and technical factors driving the asset’s price and determine if it is expected to rise during the option’s lifespan. Conducting thorough research on industry trends, company performance, and market sentiment can help form an informed opinion.
2. Strike Price Selection: The strike price of a call option represents the agreed-upon purchase price for the underlying asset. When buying call options, it is important to select an appropriate strike price based on expectations of future price movements. Choosing a strike price that is too high may result in an ineffective option, while selecting one too low may reduce potential profits.
3. Option Expiration: Call options have expiration dates, after which they become worthless if not exercised or sold before that date. Traders must consider their investment timeframe and choose options with expiration dates that align with their anticipated price movements. Longer-dated options provide more time for potential profits but also carry higher premiums.
4. Volatility Assessment: Volatility refers to how much and how quickly prices change in the underlying market. Higher volatility increases both risks and potential rewards when buying call options since larger price swings offer greater profit potential but also increase the likelihood of losses. 5. Risk Management: Like any investment strategy, buying call options involves risk management considerations such as position sizing and stop-loss orders to limit potential losses if prices move against expectations. In conclusion, buying call options can offer traders the opportunity to profit from upward price movements in an underlying asset.
Is Buying Call Options Right For You?
The decision to buy call options depends on various factors and should be carefully considered. Call options can offer significant advantages, such as limited risk and the potential for high returns. However, they also come with inherent risks that must be acknowledged.
One key consideration is your risk tolerance. If you are comfortable with taking on higher risks in pursuit of potentially greater rewards, buying call options may be suitable for you. However, if you are risk-averse and prefer more conservative investment strategies, this may not be the right path.
Another important factor is your understanding of the underlying asset and market conditions. Successful option trading requires knowledge about the specific stock or index being traded and a comprehensive understanding of market trends. If you are unfamiliar with these concepts or lack experience in options trading, it is advisable to educate yourself or seek professional guidance before entering into this market.
Additionally, time plays a crucial role in option trading. Call options have expiration dates, which means that timing is critical when buying them. You need to accurately predict price movements within a specific timeframe for your option to generate profits. This requires careful analysis and market research to increase your chances of success.
Furthermore, it is essential to have a clear investment strategy when buying call options. Without a well-defined plan, emotions can drive decisions, leading to impulsive trades and potential losses. Establishing clear goals and sticking to predetermined exit points will help mitigate risks associated with options trading.
Ultimately, whether or not buying call options is right for you will depend on your individual circumstances and investment objectives. It is crucial to thoroughly assess your risk tolerance level, knowledge of the underlying asset and market conditions, timing skills, and ability to execute a well-defined strategy before engaging in option trading.
Remember that investing always involves some degree of risk; thus, it is essential to diversify your portfolio by considering other investment instruments alongside call options if deemed appropriate by your financial goals and risk appetite.
